Dissolved Air Flotation (DAF) Plant
Usage Function
Dissolved Air Flotation is used in the treatment of wastewater for the separation of suspended solids, oils and fats, fibers, and other low-density materials, as well as for the thickening of activated sludge and sludge produced by chemical flocculation. It is employed in municipal wastewater treatment plants to remove settleable and floatable solids, improving the efficiency of existing treatment systems and ensuring flexibility throughout the entire system. In industrial wastewater treatment, DAF is used for product recovery and pollution reduction.
The patented system allows purification through dissolved air flotation combined with an initial chemical coagulation process. This process involves the pressurization of air with water and a chemical coagulation reaction to promote the rapid and efficient rise of solid particles to the surface, more effectively than a conventional DAF system.
Protection
Dissolution reactor
Dosing pumps
Construction Features
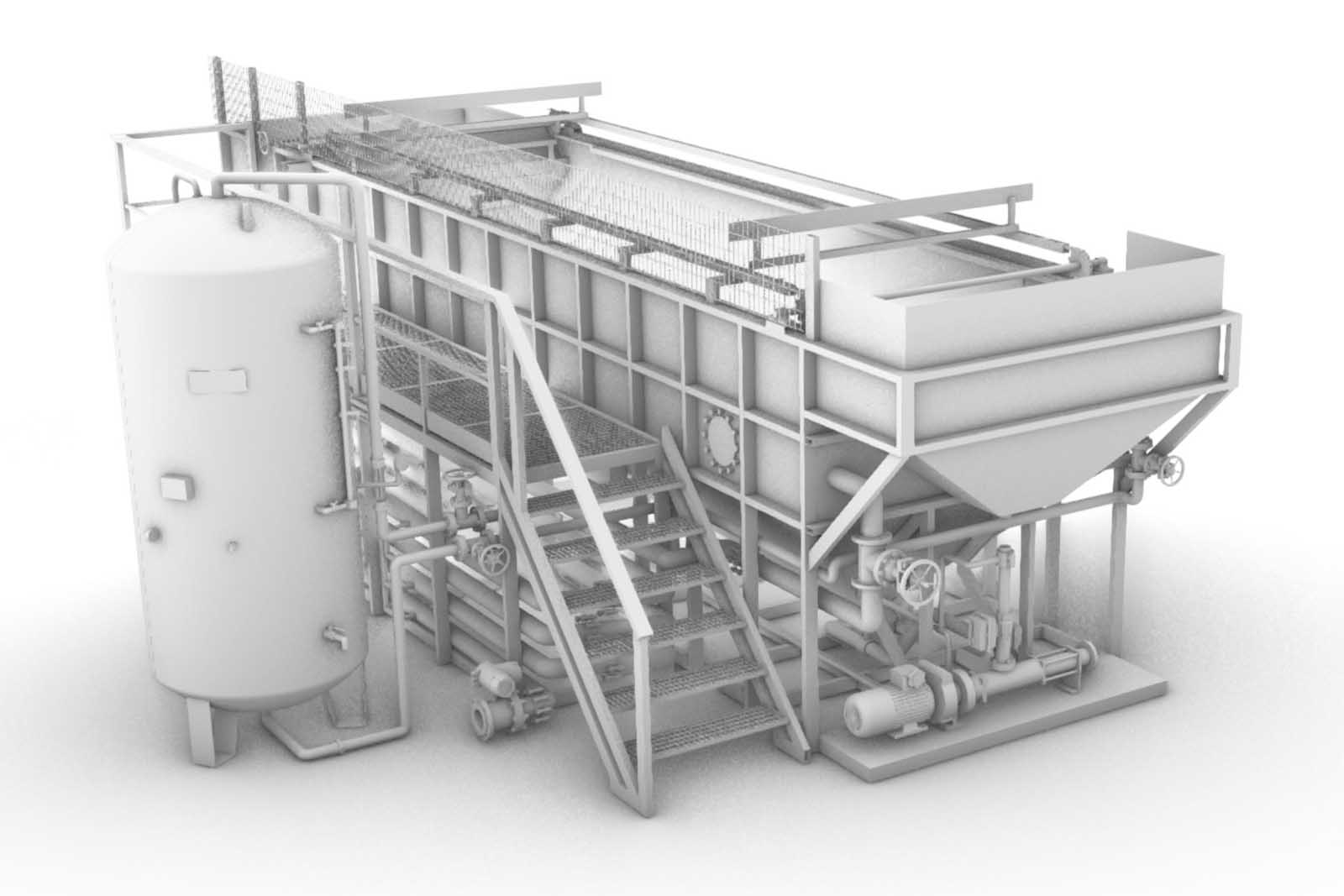
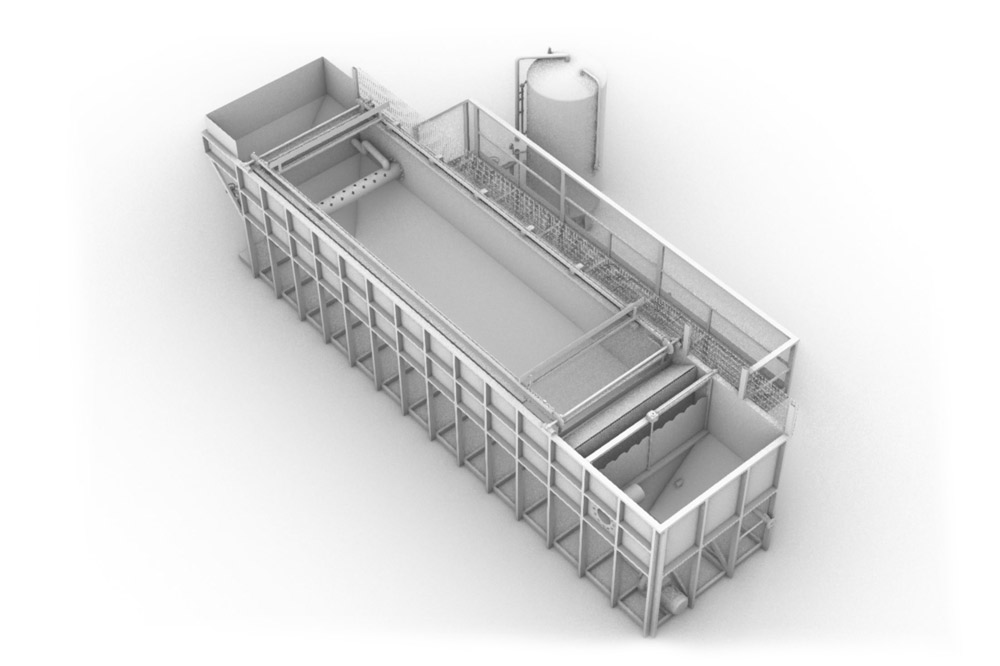
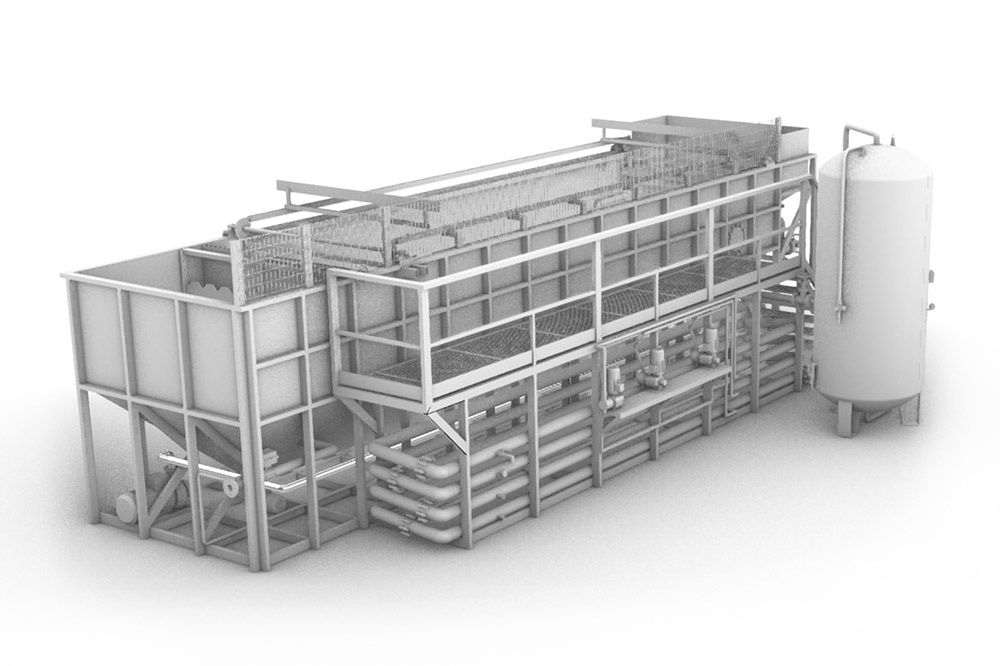
The plant consists of a flotation reactor, which is a circular or rectangular tank depending on the model, designed to contain an adequate water column that serves as a clear-flocculation chamber. The inlet, outlet, and sludge removal mechanisms are located on the surface and at the bottom. This section is composed of cleaning blades that move on the surface and at the bottom of the tank at synchronized speeds with the incoming water flow.
In the influent pipe, the water to be treated is mixed with microbubbles produced by the pressurization system through a distribution system responsible for distribution, homogenization, and contact between the “saturated” and “flocculated” mixture. The microbubbles become trapped inside the flocs and rise to the surface very quickly when they enter the “flotation chamber.” Subsequently, there is a bottom sludge scraper whose main function is to collect and convey the sludge deposited at the bottom of the flotation chamber; in the case of circular models, two “scraper arms” are used for extraction, mainly made of stainless steel and equipped with blades made of plastic material (thermoplastic resin with glass fiber reinforcement) at the end.
In the rectangular base version, the process is similar, but a “screw conveyor,” driven by a gearmotor, is used to push the sludge to the end before it is discharged by a suitable system.
The air saturation phase is crucial because it is where microbubble production that will float the particles occurs. Successful flotation depends on regulating the flotation unit so that the air-to-solids ratio has a proper flotation reaction.
It should be noted that the pressurization system consists of a medium-pressure pump, a pressurization reactor called a gas dissolution reactor where air saturation in water occurs. The air needed to further saturate the water is injected through a pressure-regulating pipe connected to the air compressor. The phase is managed by level sensors placed on the saturator side that determine whether to activate the compressor by interacting with the solenoid valve. The same principle is adopted for the recirculation pump if the water level exceeds the preset level.
The goal is to gently oversaturate the water, gently using systems in this gas dissolution reactor that purge excess supplied water.
In any case, it is necessary to have control systems and adjust the amount of air given to the water because an excess could damage the flotation process.
Advantages
- Recovery of materials such as light chemical flocs, organic discharges, light and delicate solids, fats and oils, without the use of emulsions.
- Removal of up to 90% of sludge volume.
- Reduced treatment costs.
Opzioni
- Circular/rectangular tank.
- Tank in stainless steel/cement.
- With bottom scraper (if required).
Accessories
- Reactor Tank for Dissolved Air Flotation
- Attrezzatura impianto di flottazione quale
- Central Fixed Part: Used for the removal of floated sludge.
- Support Structure for the Flotation Tank: A structure that provides support for the flotation tank.
- Rotating Bridge: Used for the installation of the paddle and rotating movable parts.
- Inspection Ladder: A ladder that allows direct inspection of the flotation tank, facilitating optimization of plant adjustments and monitoring of chemical product consumption.
- Central Cylinder: Used to separate the main flotation section from the clarified water section, which contains the extraction tubes for clarified water.
- Surface Blade: Used for the extraction of floated materials.
- Bottom Cleaning Blades: Used for continuous cleaning of the tank’s bottom and to transport accumulated sediments to the incorporated black pit.
- Telescopic Valve: Composed of a vertical tube with manual adjustment and a screw wheel for regulating the outlet height of the clarified water discharge tube installed in the recirculation tank.
- Fixed Automatic Valve: Used for discharging sedimented sludge, this valve is motorized and can be operated via a timer or manually.
- Centrifugal Pump: Used for recirculating clarified water back to the saturator.
- Various Valves: These include an interception valve placed at the exit of the clarified water tank, a non-return valve placed at the exit of the recirculation pump, a distribution valve for the saturated water, and a discharge valve for the flotation chamber.
- AISI 304 Stainless Steel Saturation Tank: This tank is equipped with upper and lower flanges.
- Pressure Gauges: Used to measure the inlet and outlet pressure.
- Pressure Reducers: Used to ensure a constant supply of air pressure.
- Safety Valves: Used to prevent pressure from reaching dangerous levels.
- Flow Meters: Used for visually detecting the flow rate of the saturated water.